Rose of Jericho: The Resurrection Plant
The ability of some lifeforms to survive in the harshest, most unfavorable environments is amazing.
Rose of Jericho, a plant capable of thriving in arid deserts, is a good example.
In this post, you will learn so many interesting things about this plant, including a very unusual characteristic that truly sets it apart.
Characteristics of Rose of Jericho
Let’s start by learning the basics about this unusual plant.
Binomial name
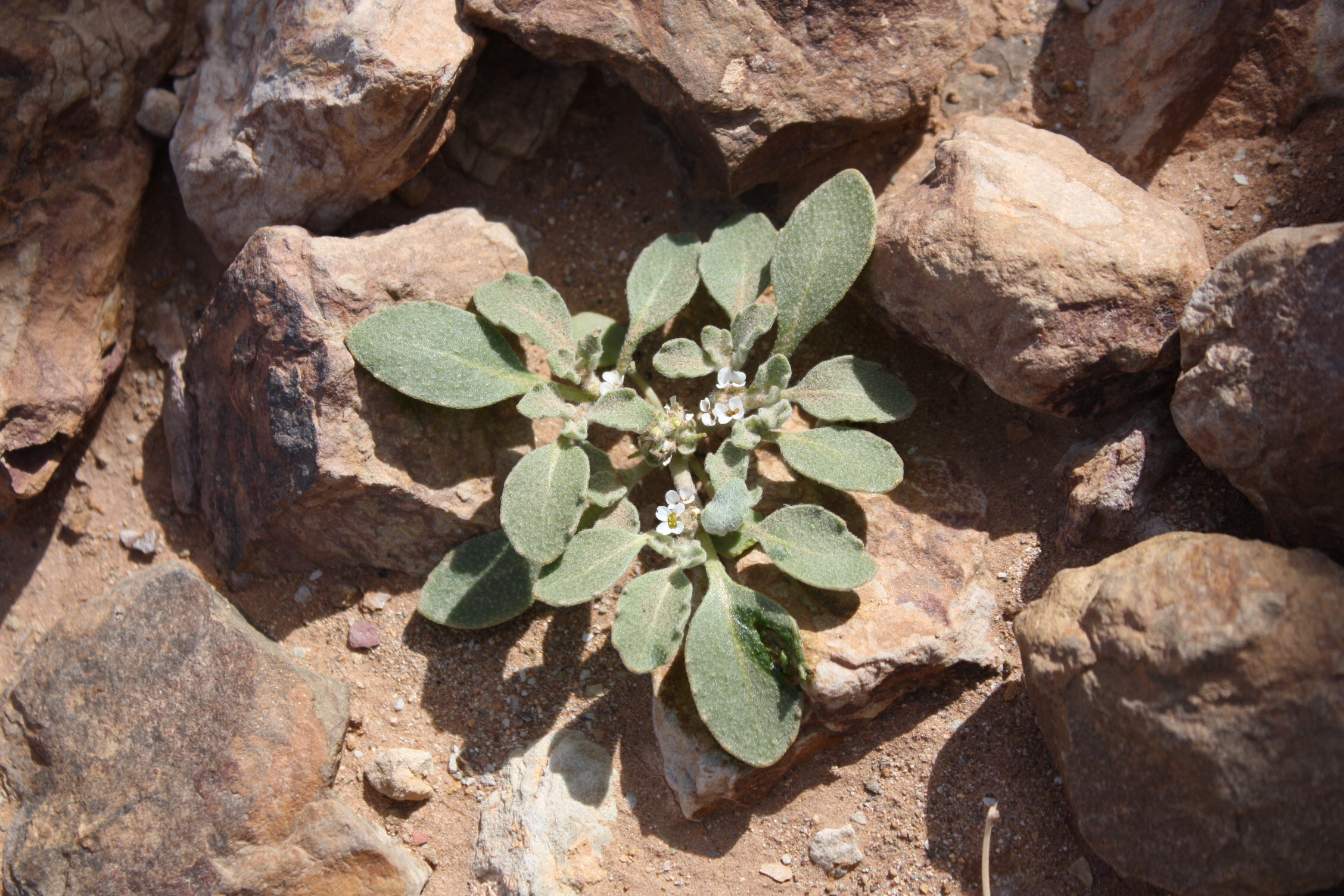
The Rose of Jericho is scientifically known as Anastatica hierochuntica and belongs to the family Brassicaceae, the same family the cabbage plant belongs to.
It’s the only species in the genus Anastatica.
Basic Characteristics
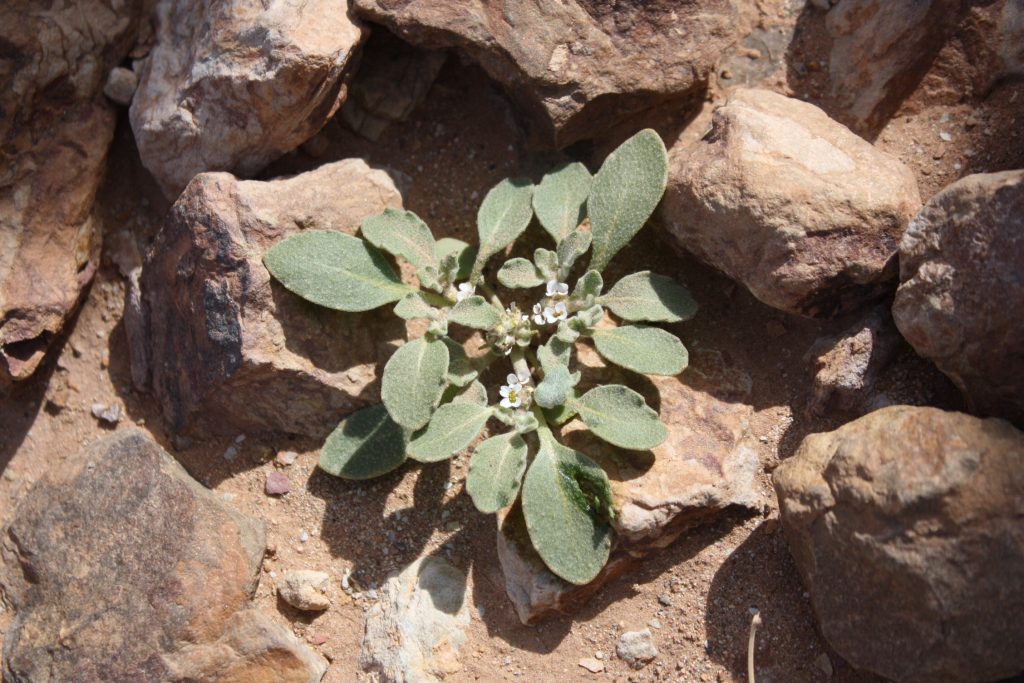
It’s a small grayish herb that typically doesn’t exceed 15 cm in height.

Own work
Author
Phil41
It’s an annual plant, meaning that it completes its life cycle from germination to seed production in one growing season and dies after producing seeds.
It produces small, white flowers and round seed pods.
Native Range & Habitat of Anastatica hierochuntica
So, where on Earth does the Rose of Jericho naturally occur?
What kind of habitats does it thrive in?
Let’s find out:
Native Range
Rose of Jericho naturally occurs in the Middle East, North Africa, and some parts of Asia.
Habitat
The plant thrives in arid environments of its native range, including the Sahara Desert, where the annual rainfall can be less than 100 mm a year.
Hygroscopic Movement: The Secret Behind The Resurrection Plant
Now we get to the most unusual characteristic of this plant, the characteristic that earns its nickname “resurrection plant”.
Curling Up to Protect The Seeds
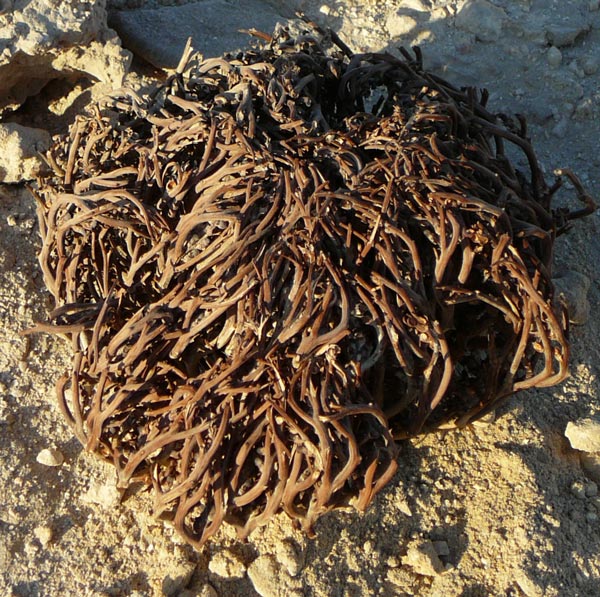
When the Anastatica hierochuntica plant bears the seeds, being an annual, dies and curls up to a ball to protect the seeds in extremely dry conditions.

Originally from de.wikipedia;
(Original text: eigenes Foto)
The curled-up plant can get carried around by the wind, so it’s considered a tumbleweed.
Hygroscopic Movement
When the rain falls on the curled-up plant, it absorbs the water and unfolds, exposing the seeds. This is called hygroscopic behavior.
As rain hits the exposed seed posts, the seeds get dropped down, absorb the water, and germinate.
This uncurling is a mechanical movement that happens as the dead plant’s tissue absorbs water. So, the plant doesn’t really resurrect.
Once the rain stops, the dead plant will curl back up, protecting any undispersed seeds until the next rainfall.
The newly germinated seeds will grow, bear flowers, produce seeds, die back, and curl up within a few weeks.
Ecological Importance of The Resurrection Plant
Let’s look into the role the resurrection plant plays in its habitat ecosystems.
Rainfall Indicator
The plant can be used as a natural rain gauge to understand the amount of rainfall a certain area receives.
The more rainfall and surface runoff an area gets, the bigger the specimens of this plant will be in that area.
On the other hand, if the Rose of Jericho plants in an area is smaller, the rainfall and surface runoff in that area is likely on the lower end.
As the plant often grows in spots where rainwater gets collected, like depressions on the ground, observing the size and distribution of this plant helps determine how much rain has fallen on a certain area.
Enrichment of Microhabitats
Anastatica hierochuntica mostly grows in depressions and runnels where rainwater accumulates. Being more moist than the surrounding areas, these spots act as microhabitats.
The plant helps turn these microhabitats suitable habitats for other small creatures like insects, spiders, and lizards by providing shelter and shade with its foliage, holding the soil together with its roots and retaining soil moisture, adding organic matter to the soil, and providing food with its seeds and decomposing organic matter.
Uses & Cultural Significance of Rose of Jericho
The Rose of Jericho has many uses for mankind and is an important part of the culture of the local people in its native range.
Uses in Traditional Medicine
The plant is used in traditional medicine in many ways.
It’s used to make childbirth easier, reduce internal bleeding in the uterus, and, in cases of miscarriage, help expel the dead fetus. It’s taken as a decoction or tea, especially in late pregnancy.
In places like Morocco and Tunisia, it’s used to treat infertility in women and strengthen the uterus.
It’s also used to treat kidney problems, urinary infections, headaches, arthritic and menstrual pain, infections like influenza, as well as conditions like epilepsy, heart disease, and depression.
The plant also can lower blood glucose levels and help repair pancreatic tissue.
Cultural Significance
In Christian traditions, the plant is called Mary’s Hand” (Kaff-e-Maryam) in Arabic; there is a legend that says that the Virgin Mary used this plant to quench her thirst and, in return, blessed it with the ability to resurrect.
Another Christian legend says that the plant died when Jesus died on the cross and was revived upon his resurrection.
The Bible mentions roses in Jericho” in the Book of Sirach (24:14), but scholars are debating whether it refers to Anastatica hierochuntica.
The plant’s ability to uncurl upon contact with water is a symbol of renewal, hope, and resilience in many cultures.
Conservation Status
There have been no significant reported threats to the Rose of Jericho plant.
The IUCN Red List considers the plant common and widespread in its native range.
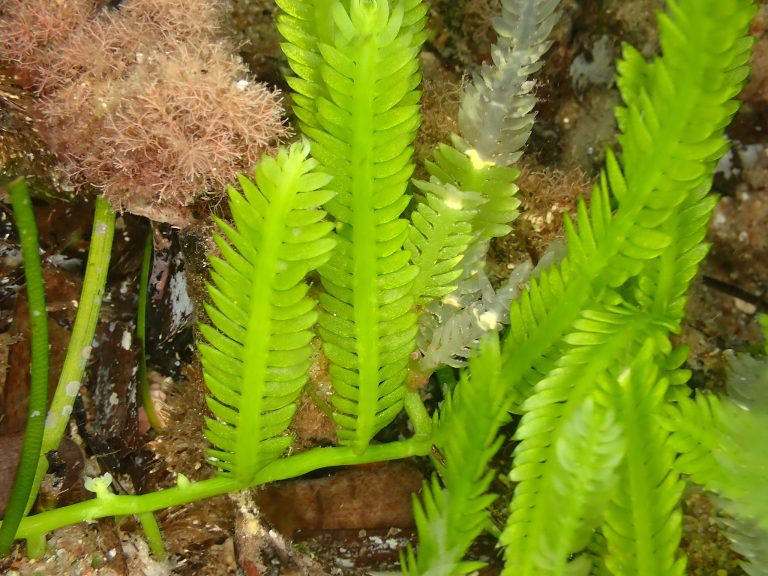
True Rose of Jericho Vs False Rose of Jericho
There is another plant, called Falae Rose of Jericho, that can be confused with the Rose of Jericho.
Let’s compare the two plants and see their differences.
Binomial name Difference
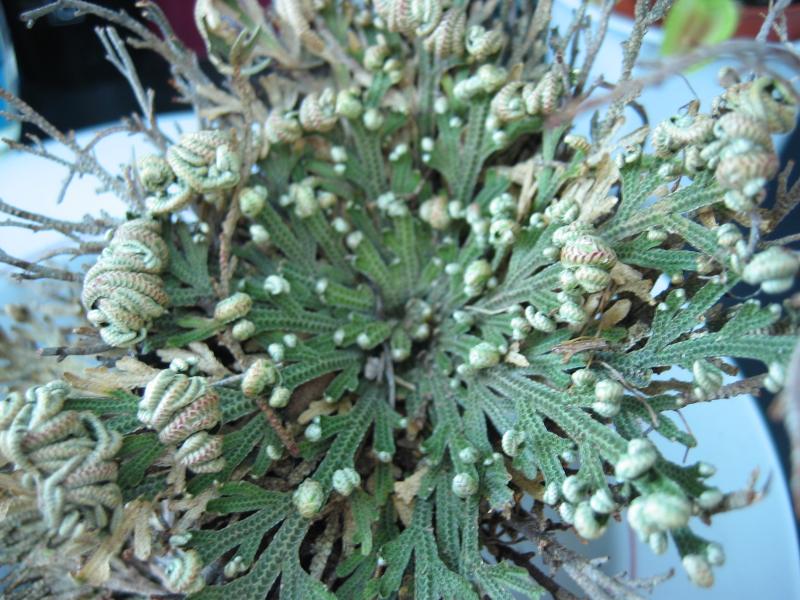
We already know that the binomial name of the Rose of Jericho is Anastatica hierochuntica, and the False Rose of Jericho is scientifically known as Selaginella lepidophylla.

Differences in Reproduction
The Rose of Jericho is a flowering plant, and bears seeds, and the False Rose of Jericho is a nonflowering plant, a spikemoss, which reproduces mostly through spores.
Differences in The Resurrection Ability
The dead and curled-up Rose of Jericho mechanically uncurls when rain falls on it but does not really come back to life, while the false Rose of Jericho, though it curls into a dried-up ball in the dry season, uses special sugars and proteins to protect its cells and comes back to life when it gets hydrated.
So, the False Rose of Jericho is a resurrection plant in the true sense of the word.
Differences in Native Range
While the Rose of Jericho is found in arid environments of the Middle East, North Africa, and some parts of Asia, the False Rose of Jericho naturally occurs in Mexico and Southwestern US.
Conclusion
Rose of Jericho is a small annual herb found in dry environments of the Middle East, North Africa, and some parts of Asia.
It quickly grows, bears flowers, goes into seed, dies, and curls up into a dry ball in the arid weather, sometimes getting blown around by wind.
When rain falls on it, it absorbs the water and uncurls, exposing the seeds to rainwater, which drops down, absorbs the rainwater, and germinates.
It acts as a natural rain gauge and enriches microhabitats in its desert home, providing shelter and food for other small animals.
It is used in traditional medicine to help with several ailments and childbirth.
It’s part of Christian traditions and legends and symbolizes renewal, hope, and resilience.
It can get confused with the False Rose of Jericho, a nonflowering spikemoss found in Mexico and the Southwestern US that can stay dried up and dormant and truly revive when hydrated.