Exploring Earth’s Biodiversity Hotspots: Important Areas for Conservation
If you are interested in contributing to protecting Earth’s environment, getting to know biodiversity hotspots is important.
These special areas are full of life forms not found anywhere else, and face serious threats.
So protecting them is crucial for keeping our planet healthy.
This post looks into what biodiversity hotspots are, why they matter globally, and why we must take action to protect them urgently.
What is a Biodiversity Hotspot?
First off, let’s see what defines a certain region on Earth as a biodiversity hotspot.
Definition and Criteria
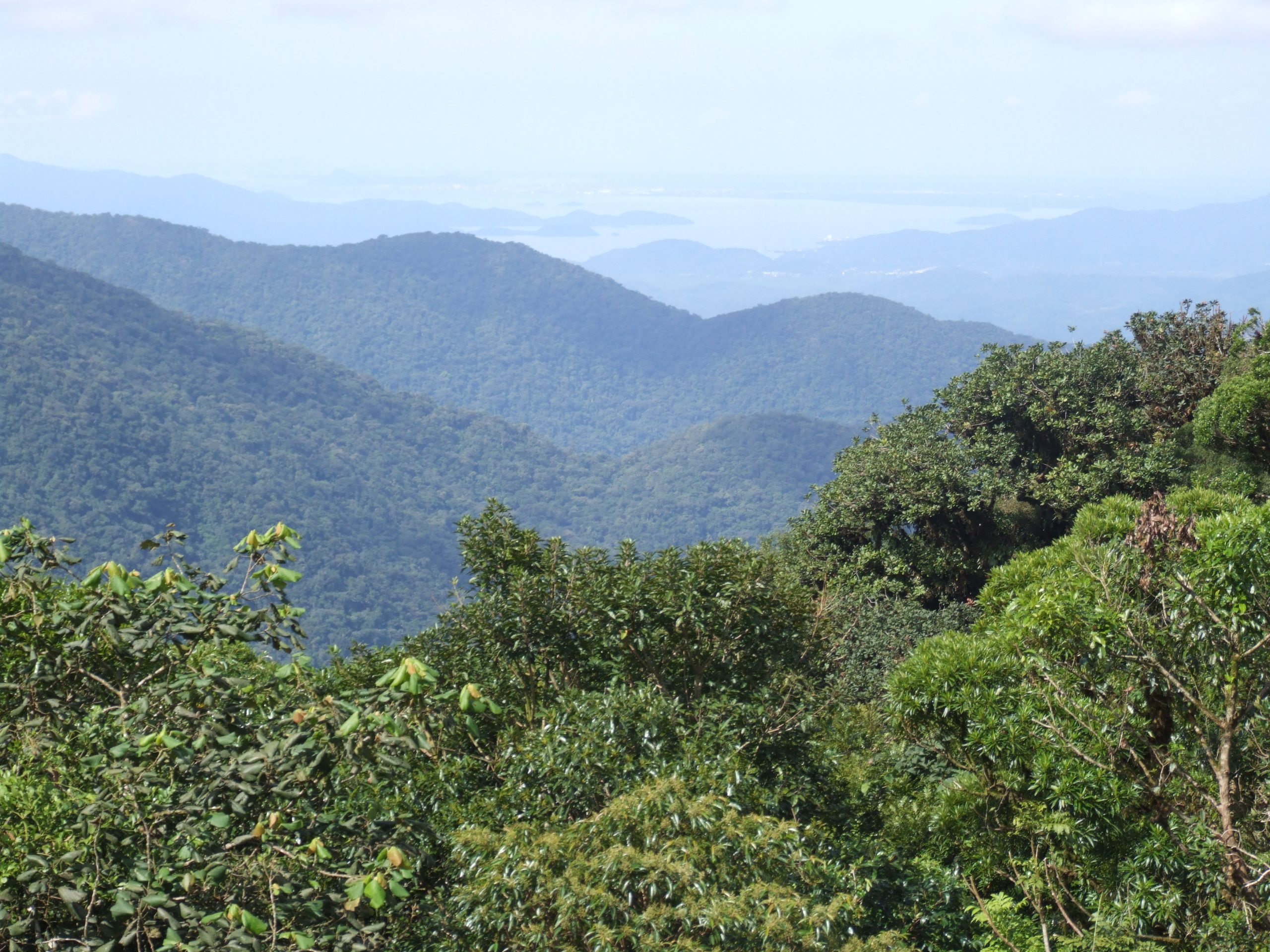
A biodiversity hotspot is a region with a high number of endemic species, species that are not found anywhere else in the world, with significant loss of their natural habitat.
An area must meet two main criteria to be considered a biodiversity hotspot: it must have at least 1,500 types of endemic plants and must have lost a minimum of 70% of its original natural vegetation.
These criteria ensure that biodiversity hotspots are vital areas for threatened species.
Importance for Global Biodiversity
A remarkable aspect of Biodiversity hotspots is that they cover only 2.3% of the Earth’s land but host more than 50% of the world’s plant species and 42% of land vertebrates as endemic species.
So, biodiversity hotspots must be an important part of the attempts to conserve biodiversity on a global level.
They act as natural laboratories for studying evolution and benefit both local communities and the planet.
Key Characteristics of Biodiversity Hotspots
Let’s delve further into the characteristics of biodiversity hotspots now.
High Species Endemism
Biodiversity hotspots are known for hosting many endemic species.
For example, 85% of the animals and 90% of the plants found in Madagascar are endemic.
There are a few reasons for this high species endemism.
Having been isolated for a long time is one of them, most hotspots being islands or isolated mountains.
Most of these hotspots are regions that highly vary topographically, having coastal areas, flat plains, mountain ranges, and so on, creating diverse ecological niches. This is another factor that contributes to high species endemism.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
Biodiversity hotspots of the world have lost much of their original habitat by now. Many of them have lost over 90% of their natural vegetation.
What remains of these habitats have mostly been broken into small, isolated areas. This disturbs natural ecological processes and puts many species at risk of extinction.
Ecological Significance
Other than the value of their high biodiversity, hotspots play a crucial role in ecological processes at a global level too.
They help absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, regulate water cycles, and conserve soil.
For example, the Tropical Andes hotspot is the main water source for millions in South America.
Major Biodiversity Hotspots Around the World
Let’s look at some of the most prominent biodiversity hotspots in the world now.
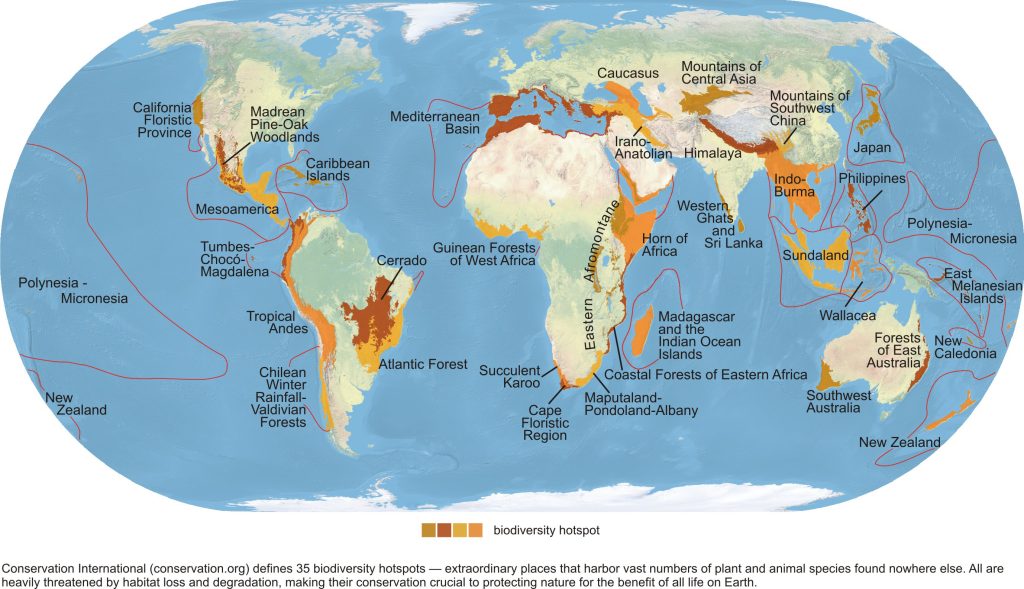
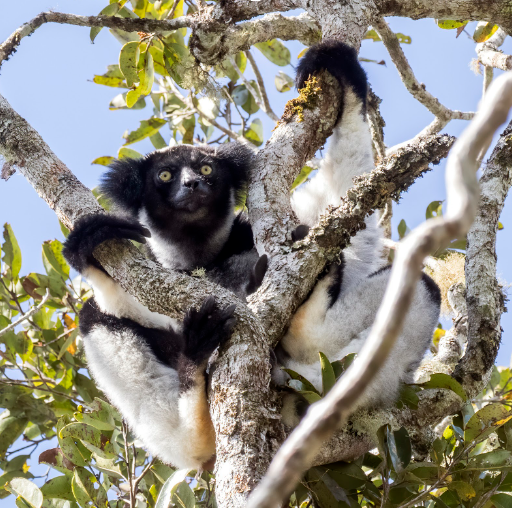
1Madagascar and Indian Ocean Islands: Known for its unique species diversity, including animals like lemurs and chameleons, this hotspot region is threatened by unsustainable farming and industrial practices.

- Brazil’s Atlantic Forest: Home to over 20,000 plant species but only about 15% of its original forest remains due to deforestation.
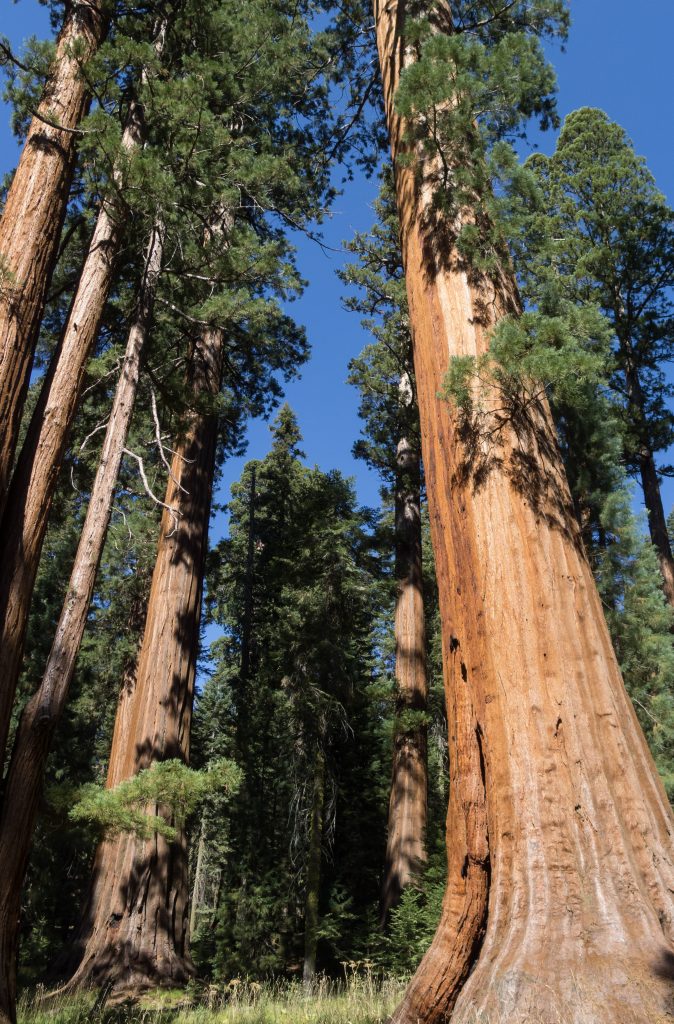
- California Floristic Province: Contains iconic trees like giant sequoias but faces threats from urbanization and wildfires.

- South Africa’s Cape Floral Region: Features around 9,000 plant species but struggles with invasive species and urban growth.
- The Philippines: Has a high number of unique species but suffers from deforestation and rapid urbanization.
- Tropical Andes: One of the richest hotspots of the world but faces threats from mining and agriculture.
Threats Faced by Biodiversity Hotspots
It’s the same characteristics that make biodiversity hotspots full of life that make them at risk.
Here are the main threats they face:
Habitat Destruction
Human activity is causing many hotspots to lose their natural environments.
Farming often requires clearing large areas of land and this destroys the habitats of many plants and animals.
Urban development also takes away habitats away from these life forms.
Industrial development, including building factories and factory operations, causes pollution and further habitat loss.
Climate Change
This is another major threat to biodiversity hotspots.
Climate change causes changes in temperatures and rainfall patterns.
Many endemic species have adapted to specific climate conditions, and these changes can compromise their survival.
Invasive Species
Invasive species are plants or animals that have been introduced to areas they are not native to, often by human activity.
These species can outcompete native species for natural resources, causing declines in native species populations.
For example, if an invasive plant spreads fast and takes over an area, it can prevent native plants from getting enough sunlight and nutrients, disrupting their growth and propagation.
This in return can topple the balance of the ecosystem.
Exploitation of Natural Resources
Many biodiversity hotspots are constantly exploited for resources like fish, timber, minerals, and water.
When these resources are extracted faster than they can be replenished, it can cause significant plant and animal population declines.
Let’s take fishing as an example. If it’s done so intensely that their natural propagation can’t keep up, it not only affects the fish populations but also other animals that prey on them.
The methods used for extracting some resources, like mining for minerals, can damage the soil, contaminate the waters, and destroy the forest cover.
This can cause plants and animal species to lose their habitats and perish.
Pollution
Pollution is another major threat to the world’s biodiversity hotspots.
The pollutants come from various sources.
The fertilizers, herbicides, and insecticides used in commercial agriculture are one such source.
They can kill native plants and animals upon contact or by being ingested.
They can get washed into the natural water sources during rain, potentially causing great damage to the aquatic ecosystems.
Also, industrial waste and plastic waste cause damage to the fragile ecosystems within the biodiversity hotspots too.
Conservation Efforts in Biodiversity Hotspots
Now it’s time for us to look into the efforts to protect these threatened biodiversity hotspots.
International Initiatives
There are global conservation organizations that recognize the importance of biodiversity hotspots.
The Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund (CEPF) is one such organization. It provides grants to other organizations that work on protecting the hotspots by establishing protected zones and promoting sustainable practices.
Local and Community-Based Conservation
Involving local communities is a must for conserving biodiversity hotspots.
Efforts that connect conservation attempts with the livelihoods of local communities have shown positive results.
For example, the involvement of local communities protecting marine areas in Madagascar helps preserve coral reefs while supporting local fishing.
Sustainable Development Approaches
Adopting a sustainable approach to development is vital for the success of conserving biodiversity hotspots in the long run.
This includes eco-friendly farming and industrial practices, responsible tourism, and implementing payment schemes for ecosystem services these hotspots provide to raise funds needed for conservation.
The Future of Biodiversity Hotspots
So, what does the future hold for Earth’s biodiversity hotspots?
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change threatens biodiversity hotspots, changing habitats faster than many species can adapt.
On the other hand, disruption to the hotspots contributes to climate change.
Monitoring these changes and making amends is essential for effective conservation.
Restoration and Rewilding Projects
As habitat loss has become a major threat, attempts at restoration are becoming more common.
Rewilding attempts aim to return ecosystems to their natural state, helping recover their lost biodiversity and making them more resilient.
Importance of Continued Research and Monitoring
Continuous research in hotspots is crucial as they provide guidance for conservation efforts.
New technologies help understand biodiversity better, and long-term monitoring is necessary to track the health of ecosystems and evaluate the success of conservation attempts.
How You Can Help Protect Biodiversity Hotspots
As the members of the most intelligent animal species of planet Earth and the species solely responsible for the destruction of its biodiversity hotspots, we all bear undeniable responsibility towards their conservation.
- Supporting Conservation Organizations: You can help by donating to or volunteering with organizations focused on protecting biodiversity hotspots.
- Sustainable Travel and Tourism: When traveling, choose eco-friendly options and support local conservation.
- Making Eco-Friendly Consumer Choices: Choose sustainably manufactured products, and avoid those that contribute to habitat destruction as they are manufactured.
Conclusion
Biodiversity hotspots are important areas of the Earth that host a significant number of endemic species and play a vital role in global biodiversity.
These regions, covering just a tiny portion of the Earth’s land, face serious threats such as habitat loss, climate change, and pollution.
Protecting these hotspots is essential for preserving the planet’s health and supporting ecological processes.
Conservation efforts, including international initiatives and community involvement, are necessary to protect these important areas.
By understanding their significance and taking action, we can contribute to the protection of biodiversity hotspots for future generations.







